Tri par arbre : tri à l’aide d’un arbre de recherche binaire. Complexité temporelle – O(n²). Dans un tel arbre, chaque nœud à gauche a des nombres inférieurs au nœud, à droite il y en a plus que le nœud, en venant de la racine et en imprimant les valeurs de gauche à droite, on obtient une liste triée de nombres . Surprenant, non ?
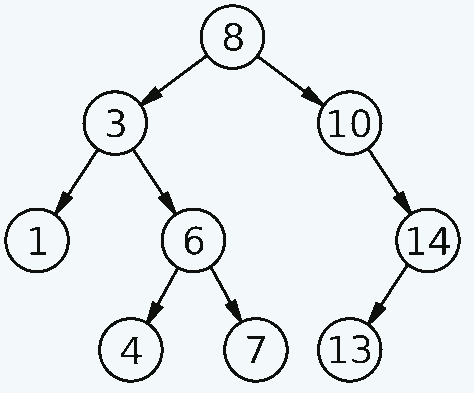
Considérez l’arbre de recherche binaire :
Derrick Coetzee (domaine public)
Essayez de lire manuellement les nombres en partant de l’avant-dernier nœud gauche du coin inférieur gauche, pour chaque nœud à gauche – un nœud – à droite.
Cela ressemblera à ceci :
- Avant-dernier nœud en bas à gauche – 3.
- Il a une branche gauche – 1.
- Prenez ce numéro (1)
- Ensuite, nous prenons le sommet 3 (1, 3)
- À droite se trouve la branche 6, mais elle contient des branches. Par conséquent, nous le lisons de la même manière.
- Branche gauche du nœud 6 numéro 4 (1, 3, 4)
- Le nœud lui-même est 6 (1, 3, 4, 6)
- Droite 7 (1, 3, 4, 6, 7)
- Montez jusqu’au nœud racine – 8 (1,3, 4,6, 7, 8)
- Nous imprimons tout à droite par analogie
- Nous obtenons la liste finale – 1, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 10, 13, 14
Pour implémenter l’algorithme dans le code, vous aurez besoin de deux fonctions :
- Assembler un arbre de recherche binaire
- Imprimer l’arbre de recherche binaire dans le bon ordre
L’arbre binaire de recherche est assemblé de la même manière qu’il est lu, un numéro est attaché à chaque nœud à gauche ou à droite, selon qu’il est inférieur ou supérieur.
Exemple en Lua :
function Node:new(value, lhs, rhs)
output = {}
setmetatable(output, self)
self.__index = self
output.value = value
output.lhs = lhs
output.rhs = rhs
output.counter = 1
return output
end
function Node:Increment()
self.counter = self.counter + 1
end
function Node:Insert(value)
if self.lhs ~= nil and self.lhs.value > value then
self.lhs:Insert(value)
return
end
if self.rhs ~= nil and self.rhs.value < value then
self.rhs:Insert(value)
return
end
if self.value == value then
self:Increment()
return
elseif self.value > value then
if self.lhs == nil then
self.lhs = Node:new(value, nil, nil)
else
self.lhs:Insert(value)
end
return
else
if self.rhs == nil then
self.rhs = Node:new(value, nil, nil)
else
self.rhs:Insert(value)
end
return
end
end
function Node:InOrder(output)
if self.lhs ~= nil then
output = self.lhs:InOrder(output)
end
output = self:printSelf(output)
if self.rhs ~= nil then
output = self.rhs:InOrder(output)
end
return output
end
function Node:printSelf(output)
for i=0,self.counter-1 do
output = output .. tostring(self.value) .. " "
end
return output
end
function PrintArray(numbers)
output = ""
for i=0,#numbers do
output = output .. tostring(numbers[i]) .. " "
end
print(output)
end
function Treesort(numbers)
rootNode = Node:new(numbers[0], nil, nil)
for i=1,#numbers do
rootNode:Insert(numbers[i])
end
print(rootNode:InOrder(""))
end
numbersCount = 10
maxNumber = 9
numbers = {}
for i=0,numbersCount-1 do
numbers[i] = math.random(0, maxNumber)
end
PrintArray(numbers)
Treesort(numbers)Важный нюанс что для чисел которые равны вершине придумано множество интересных механизмов подцепления к ноде, я же просто добавил счетчик к классу вершины, при распечатке числа возвращаются по счетчику.
Ссылки
https://gitlab.com/demensdeum/algorithms/-/tree/master/sortAlgorithms/treesort
Источники
Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree (LeetCode 108. Algorithm Explained) – YouTube
Sorting algorithms/Tree sort on a linked list – Rosetta Code
How to handle duplicates in Binary Search Tree? – GeeksforGeeks
Tree Sort | GeeksforGeeks – YouTube