Classificação em árvore – classificação usando uma árvore de pesquisa binária. Complexidade de tempo – O(n²). Nessa árvore, cada nó da esquerda tem números menores que o nó, à direita há mais que o nó, ao vir da raiz e imprimir os valores da esquerda para a direita, obtemos uma lista ordenada de números . Surpreendente, certo?
Considere o diagrama de árvore de pesquisa binária:
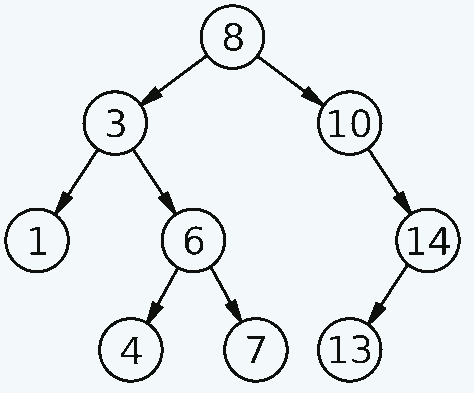
Derrick Coetzee (domínio público)
Tente ler manualmente os números começando pelo penúltimo nó esquerdo do canto inferior esquerdo, para cada nó à esquerda – um nó – à direita.
Ficará assim:
- Penúltimo nó no canto inferior esquerdo – 3.
- Tem um ramo esquerdo – 1.
- Pegue este número (1)
- Em seguida, pegamos o vértice 3 (1, 3)
- À direita está o ramo 6, mas contém ramos. Portanto, lemos da mesma maneira.
- Ramo esquerdo do nó 6 número 4 (1, 3, 4)
- O próprio nó é 6 (1, 3, 4, 6)
- Direita 7 (1, 3, 4, 6, 7)
- Vá até o nó raiz – 8 (1,3, 4,6, 7, 8)
- Imprimimos tudo à direita por analogia
- Obtemos a lista final – 1, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 10, 13, 14
Para implementar o algoritmo em código, você precisará de duas funções:
- Montando uma árvore de pesquisa binária
- Imprimindo a árvore de pesquisa binária na ordem correta
A árvore binária de busca é montada da mesma forma que é lida, um número é anexado a cada nó à esquerda ou à direita, dependendo se é menor ou maior.
Exemplo em Lua:
function Node:new(value, lhs, rhs)
output = {}
setmetatable(output, self)
self.__index = self
output.value = value
output.lhs = lhs
output.rhs = rhs
output.counter = 1
return output
end
function Node:Increment()
self.counter = self.counter + 1
end
function Node:Insert(value)
if self.lhs ~= nil and self.lhs.value > value then
self.lhs:Insert(value)
return
end
if self.rhs ~= nil and self.rhs.value < value then
self.rhs:Insert(value)
return
end
if self.value == value then
self:Increment()
return
elseif self.value > value then
if self.lhs == nil then
self.lhs = Node:new(value, nil, nil)
else
self.lhs:Insert(value)
end
return
else
if self.rhs == nil then
self.rhs = Node:new(value, nil, nil)
else
self.rhs:Insert(value)
end
return
end
end
function Node:InOrder(output)
if self.lhs ~= nil then
output = self.lhs:InOrder(output)
end
output = self:printSelf(output)
if self.rhs ~= nil then
output = self.rhs:InOrder(output)
end
return output
end
function Node:printSelf(output)
for i=0,self.counter-1 do
output = output .. tostring(self.value) .. " "
end
return output
end
function PrintArray(numbers)
output = ""
for i=0,#numbers do
output = output .. tostring(numbers[i]) .. " "
end
print(output)
end
function Treesort(numbers)
rootNode = Node:new(numbers[0], nil, nil)
for i=1,#numbers do
rootNode:Insert(numbers[i])
end
print(rootNode:InOrder(""))
end
numbersCount = 10
maxNumber = 9
numbers = {}
for i=0,numbersCount-1 do
numbers[i] = math.random(0, maxNumber)
end
PrintArray(numbers)
Treesort(numbers)Важный нюанс что для чисел которые равны вершине придумано множество интересных механизмов подцепления к ноде, я же просто добавил счетчик к классу вершины, при распечатке числа возвращаются по счетчику.
Ссылки
https://gitlab.com/demensdeum/algorithms/-/tree/master/sortAlgorithms/treesort
Источники
Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree (LeetCode 108. Algorithm Explained) – YouTube
Sorting algorithms/Tree sort on a linked list – Rosetta Code
How to handle duplicates in Binary Search Tree? – GeeksforGeeks
Tree Sort | GeeksforGeeks – YouTube